Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
According to the U.S. Department of health and Human Services, up to 5 million women in the United States have PCOS.
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
- It is a complex hormone disorder that affects up to 13% of young women.
- “Polycystic” means your ovaries may have many “cysts” on them. These cysts are not visible to you, but a doctor can see them on your ultrasound pictures.
- Symptoms can include: unpredictable periods, very heavy periods, periods that are too close together or more than 30 days apart, weight gain, acne that is hard to get rid of, and/or unwanted hair on chin/chest/upper thighs.
- Doctors and scientists are working on understanding why some young girls develop PCOS.
- PCOS may have a genetic component to it, which means it can run in families.
What causes PCOS?
Several processes are believed to happen together in PCOS. These include “insulin resistance”, “high androgen levels” and “irregular periods”. Let’s break these terms down:
- “Insulin resistance”: Your body takes sugar, or “glucose”, from the food you eat. It uses glucose to power up your cells to do their job. Your body also makes insulin, a hormone that helps push glucose inside your cells so they can use it. If you have PCOS your insulin can’t “push” glucose inside your cells. This causes glucose to “pile up” instead. Your body tries to make more insulin to help, which can cause weight gain and obesity. The “pile up” of glucose in your body can also cause prediabetes & diabetes down the road.
- “High androgen levels”: Androgens are “male” hormones that every female’s body makes. If you have PCOS your body makes too much of the hormones. This is why you may notice too much hair in unwanted places and stubborn acne that is hard to treat.
- “Irregular periods”: Periods may come at different times each month, happen several times a month, or skip months. High androgen levels can contribute to your periods being irregular.
How is PCOS diagnosed?
- The doctor will ask questions about your health and your periods.
- You may need an exam during the visit.
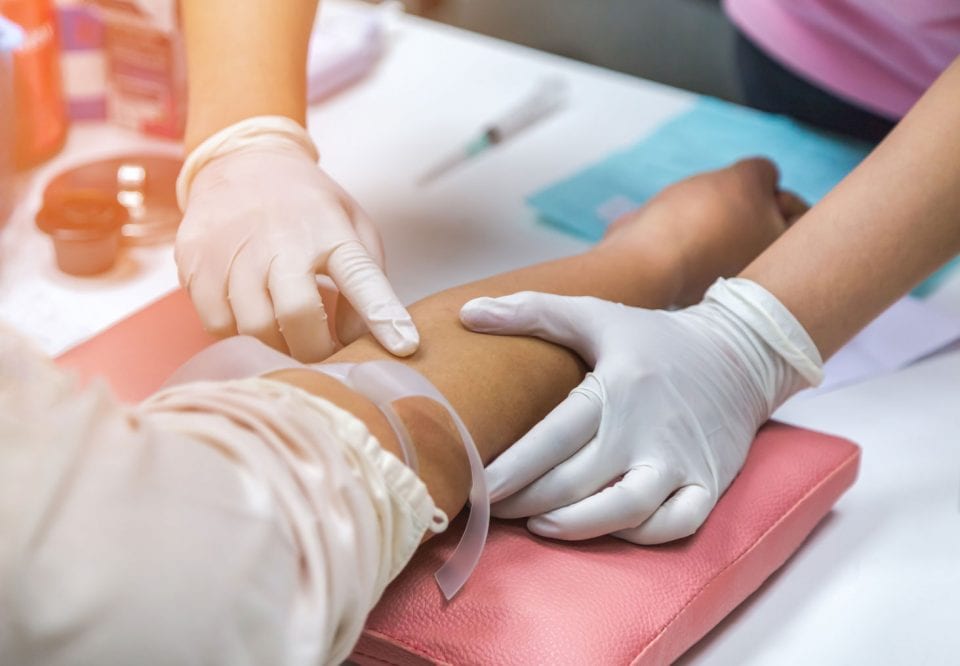
- Blood tests are done to check hormone levels.
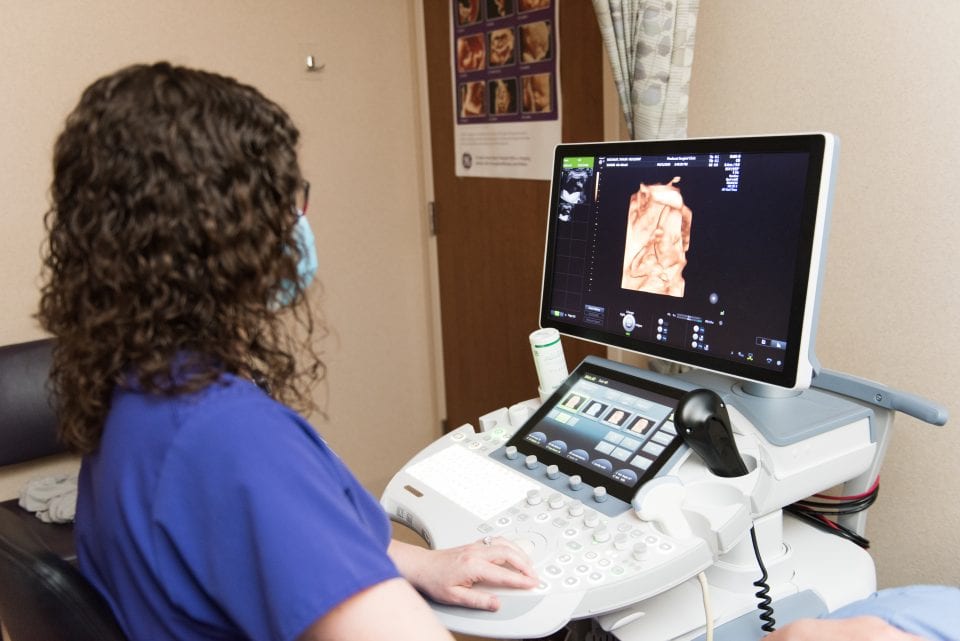
- An ultrasound may be needed. It is a painless test where images are taken of your female organs. These pictures show doctors how your ovaries, fallopian tubes and uterus look and function.
How is PCOS treated?
- Diet and Exercise – weight loss & eating healthy are key in managing PCOS. A healthy lifestyle can help make periods regular. It can help with acne and unwanted hair growth. Nutritional counseling is a great resource that can help you make important lifestyle changes.
- Birth control pills – hormones inside birth control pills can help bring on a period if you have not had one in a while, make your periods regular, make you bleed less when you have a period, and shorten the number of days your period lasts. The pills also keep uterus lining thin, which reduces the risk for developing uterine cancer in the future. If you struggle with acne, you may notice improvement of your skin. It is important you take the birth control pill at the same time every day to keep hormone levels in your body steady.
- Metformin – pills usually prescribed to treat diabetes. Metformin helps your body respond correctly to higher blood sugar levels. It ensures the insulin your body makes brings down your blood sugar levels. Your doctor may prescribe Metformin and birth control pills together for better management of PCOS.
- Your gynecologist will see you back a few months after you start the Metformin and/or birth control pills to see how you are doing.
Why is treating PCOS important?
- Left untreated, PCOS puts you at higher risk of having high cholesterol, heart disease, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, cancer of the uterus, infertility and recurrent miscarriages.
- Diet, exercise and medication therapy can successfully manage PCOS, give you relieve of bothersome symptoms and keep you healthy in the long run.
- It is important that you ask the doctor any questions you may have about managing PCOS.
Schedule An Appointment
Make an appointment with one of our OB-GYN specialists today.
Our Women’s Comprehensive Health Providers
Leading OB-GYNs in Pinehurst, Southern Pines, Fayetteville, NC & Beyond.
Gynecologic Ultrasounds
Gynecologic ultrasounds performed at our nationally-accredited ultrasound laboratory may also be used to diagnose PCOS.
Laboratory
For patient convenience we have a lab on the premises and we perform most of our lab testing on site.
Pinehurst Surgical Clinic is a multi-specialty clinic comprised of ten specialty centers located in a state-of-the-art surgical facility in Pinehurst, NC. Our OB GYN specialists serve patients in Pinehurst, Sanford, Fayetteville, Rockingham, Lillington, Montgomery, and all surrounding areas throughout North Carolina, South Carolina, and beyond.